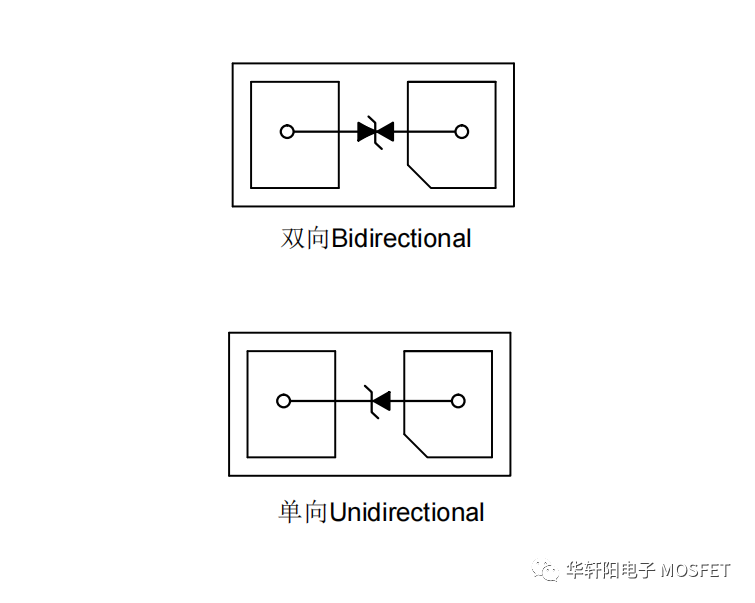
Unidirectional TVS can only conduct current in one direction, usually guiding the current to ground or other low potential points when the voltage is too high.
Bidirectional TVS can conduct current in two directions and is suitable for applications that require bidirectional protection, such as communication or signal lines, where signals may appear in the form of pulses in both positive and negative directions.
However, in general, for most applications, it is beneficial to choose unidirectional TVS as much as possible, for the following reasons:
Performance characteristics: Unidirectional TVS usually outperforms bidirectional TVS in terms of protection characteristics. They focus on voltage protection in one direction, resulting in faster and more accurate response in that direction. This is crucial for protecting sensitive electronic components as they may be more sensitive to overvoltage.
Reliability: Unidirectional TVS typically have higher voltage tolerance in one direction. Due to the protection of bidirectional TVS in both directions, their design may compromise in each direction, resulting in a decrease in overall performance and reliability.
Design simplification: Using unidirectional TVS can simplify circuit design. For most applications, only unidirectional overvoltage protection needs to be considered, so using unidirectional TVS can reduce design complexity.
Performance advantage: Unidirectional TVS typically have lower voltage cutoff and higher current capacity in its focused direction. This means that when overvoltage events occur, they can more effectively absorb and disperse electrical energy, providing better protection.
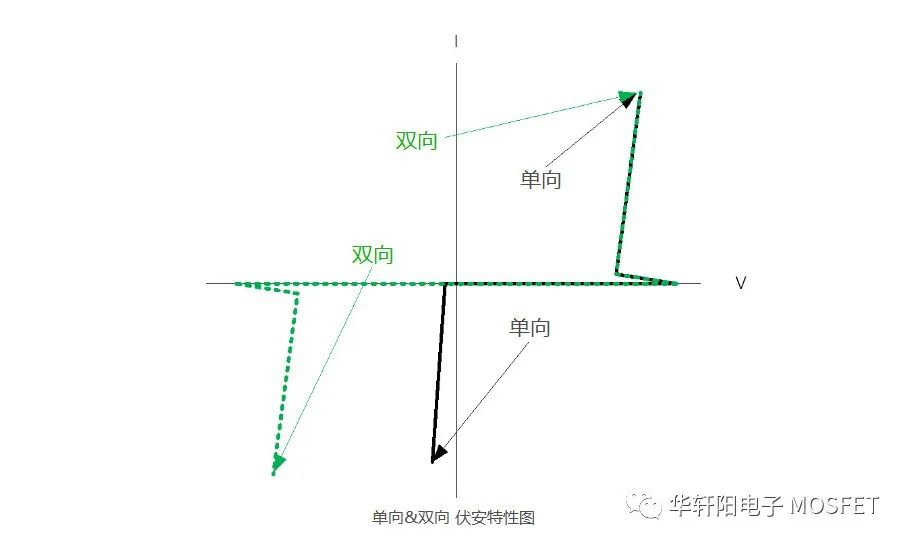
It should be noted that in certain specific applications, bidirectional protection may be required, and choosing bidirectional TVS is appropriate. However, for most cases, choosing unidirectional TVS as much as possible can provide better performance. When selecting models, you should make choices based on specific application requirements and circuit characteristics to be protected.